QuestDB Docker
High performance time series
Superior developer experience with SQL and time series extensions. Speed and reliability to solve ingestion speed bottlenecks.
Demo
Docker
docker run -d --name questdb \
-p 9000:9000 -p 9009:9009 -p 8812:8812 -p 9003:9003 \
questdb/questdb:7.3.7
Create my first dataset
Creating a table
CREATE TABLE sensors (ID LONG, make STRING, city STRING);
Inserting data
INSERT INTO sensors
SELECT
x ID, --increasing integer
rnd_str('Eberle', 'Honeywell', 'Omron', 'United Automation', 'RS Pro') make,
rnd_str('New York', 'Miami', 'Boston', 'Chicago', 'San Francisco') city
FROM long_sequence(10000) x;
'sensors';
CREATE TABLE readings
AS(
SELECT
x ID,
timestamp_sequence(to_timestamp('2019-10-17T00:00:00', 'yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss'), rnd_long(1,10,0) * 100000L) ts,
rnd_double(0)*8 + 15 temp,
rnd_long(0, 10000, 0) sensorId
FROM long_sequence(10000000) x)
TIMESTAMP(ts)
PARTITION BY MONTH;
Running queries
readings;
SELECT count() FROM readings;
SELECT avg(temp) FROM readings;
SELECT *
FROM readings
JOIN(
SELECT ID sensId, make, city
FROM sensors)
ON readings.sensorId = sensId;
# Aggregation keyed by city
SELECT city, max(temp)
FROM readings
JOIN(
SELECT ID sensId, city
FROM sensors) a
ON readings.sensorId = a.sensId;
# Aggregation by hourly time buckets
SELECT ts, city, make, avg(temp)
FROM readings timestamp(ts)
JOIN
(SELECT ID sensId, city, make
FROM sensors
WHERE city='Miami' AND make='Omron') a
ON readings.sensorId = a.sensId
WHERE ts IN '2019-10-21;1d' -- this is an interval between 2019/10/21 and the next day
SAMPLE BY 1h -- aggregation by hourly time buckets
ALIGN TO CALENDAR; -- align the ts with the start of the hour (hh:00:00)
Deleting tables
DROP TABLE readings;
DROP TABLE sensors;
Connect
HTTP REST API
curl -F data=@data.csv http://localhost:9000/imp
Runtime Environment
C++
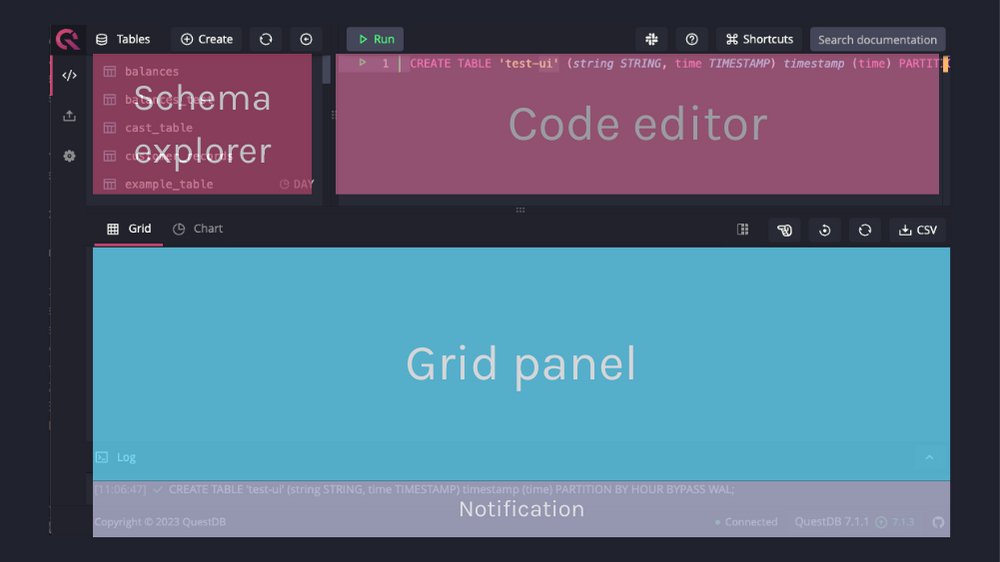
Screenshots